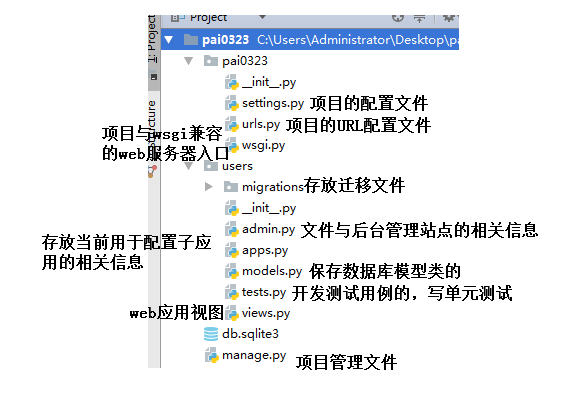
在上一篇的基礎上,我已經成功地獲取了用戶的輸入信息,下面我希望將用戶的值進行處理之后然后返回一個頁面給用戶
urls.py和前面一樣
"""
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from MyApp1 import views
urlpatterns = [
# url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^index/', views.index),
]views.py里面我新創建一個列表,把字典結構的數據放進去,然后通過render發送回去
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
USERLIST=[]
def index(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
u=request.POST.get('user')
e=request.POST.get('email')
print(u,e)
temp={'user':u,'email':e}
USERLIST.append(temp)
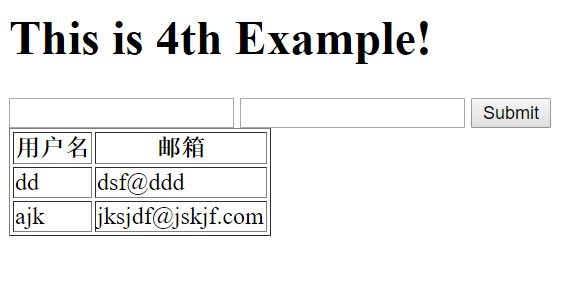
return render(request,'index.html',{'data':USERLIST})index.html 這里有一個特殊的for使用,他其實是轉換為對應的python命令,執行之后,然后把渲染后的html頁面發回給用戶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is 4th Example!</h1>
<form action="/index/" method="post">
<input type="text" name="user">
<input type="email" name="email">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<table border="1">
<th>用戶名</th>
<th>郵箱</th>
<tr>
{% for item in data %}
<td> {{ item.user }}</td>
<td> {{ item.email }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
</html>結果如下所示。
因為目前所有的數據都保存在內存里,如果重啟Django,這些數據都會丟失。
如果需要長久保存,我們需要把數據保存在數據庫了。