1. Basic definitions for Apache POI library
This section briefly describe about basic classes used during Excel Read and Write.
HSSFis prefixed before the class name to indicate operations related to a Microsoft Excel 2003 file.XSSFis prefixed before the class name to indicate operations related to a Microsoft Excel 2007 file or later.XSSFWorkbookandHSSFWorkbookare classes which act as an Excel WorkbookHSSFSheetandXSSFSheetare classes which act as an Excel WorksheetRowdefines an Excel rowCelldefines an Excel cell addressed in reference to a row.
2. Download Apache POI
Apache POI library is easily available using Maven Dependencies.
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.15</version>
</dependency>3. Apache POI library – Writing a Simple Excel
The below code shows how to write a simple Excel file using Apache POI libraries. The code uses a 2 dimensional data array to hold the data. The data is written to a XSSFWorkbook object. XSSFSheet is the work sheet being worked on. The code is as shown below:
ApachePOIExcelWrite.java
package com.mkyong;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ApachePOIExcelWrite {
private static final String FILE_NAME = "/tmp/MyFirstExcel.xlsx";
public static void main(String[] args) {
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Datatypes in Java");
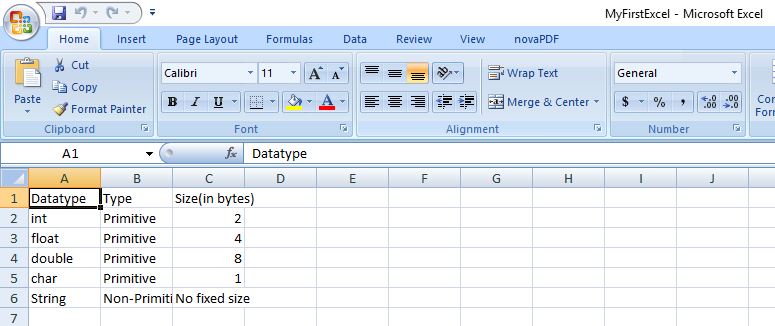
Object[][] datatypes = {
{"Datatype", "Type", "Size(in bytes)"},
{"int", "Primitive", 2},
{"float", "Primitive", 4},
{"double", "Primitive", 8},
{"char", "Primitive", 1},
{"String", "Non-Primitive", "No fixed size"}
};
int rowNum = 0;
System.out.println("Creating excel");
for (Object[] datatype : datatypes) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum++);
int colNum = 0;
for (Object field : datatype) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(colNum++);
if (field instanceof String) {
cell.setCellValue((String) field);
} else if (field instanceof Integer) {
cell.setCellValue((Integer) field);
}
}
}
try {
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(FILE_NAME);
workbook.write(outputStream);
workbook.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Done");
}
}On executing the above code, you get below excel as an output.
4. Apache POI library – Reading an Excel file
The below code explains how to read an Excel file using Apache POI libraries. The function getCellTypeEnum is deprecated in version 3.15 and will be renamed to getCellType from version 4.0 onwards.
ApachePOIExcelRead.java
package com.mkyong;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ApachePOIExcelRead {
private static final String FILE_NAME = "/tmp/MyFirstExcel.xlsx";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream excelFile = new FileInputStream(new File(FILE_NAME));
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(excelFile);
Sheet datatypeSheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> iterator = datatypeSheet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Row currentRow = iterator.next();
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = currentRow.iterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell currentCell = cellIterator.next();
//getCellTypeEnum shown as deprecated for version 3.15
//getCellTypeEnum ill be renamed to getCellType starting from version 4.0
if (currentCell.getCellTypeEnum() == CellType.STRING) {
System.out.print(currentCell.getStringCellValue() + "--");
} else if (currentCell.getCellTypeEnum() == CellType.NUMERIC) {
System.out.print(currentCell.getNumericCellValue() + "--");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}On executing the above code, you get the below output.
Datatype--Type--Size(in bytes)--
int--Primitive--2.0--
float--Primitive--4.0--
double--Primitive--8.0--
char--Primitive--1.0--
String--Non-Primitive--No fixed size--