SQLite 數據庫存儲
標簽: SQLiteDatabase
1、SQLite數據庫簡介
SQLite 是一款輕量級的關系型數據庫,它的運算速度非常快,占用資源也非常少。通常只需要幾百KB 的內存就夠了,因而特別適用于移動設備上。
2、數據庫的創建簡介
Android 為了讓我們非常方便的管理一個數據庫,專門提供一個SQLiteOpenHelper幫助類,借助這個類我們可以對數據庫進行創建,升級。
1)SQLiteOpenHelper 是一個抽象類,這意味著我們使用它的話就需要創建一個自己的幫助類來繼承它。
2) SQLiteOpenHelper 有兩個抽象方法 onCreat() onUpgrade() ,我們必須在自己的幫助類里面來重寫它,實現創建和升級的代碼邏輯。
3)SQLiteOpenHelper 還有兩個非常重要的實例方法,getReadableDataase() WritableDatabase() 這兩個方法都創建或打開一個數據庫(已存在),并返回一個可以對數據庫進行讀寫的對象。
4)當磁盤滿的時候, getReadableDataase 將以只讀的形式返回數據庫對象,WritableDatabase 會出現錯誤
5)SQLiteOpenHelper 有兩個構造方法可以重寫,一般使用參數少一點的那個即可。四個參數:
第一個參數 Context : 必須有它才能對數據庫進行操作
第二個參數:數據庫名,創建數據庫時使用的名字
第三個參數:允許我們在查詢時返回的Cursor ,一般傳入null
第四個參數:當前數據庫的版本號,可用于數據庫升級。
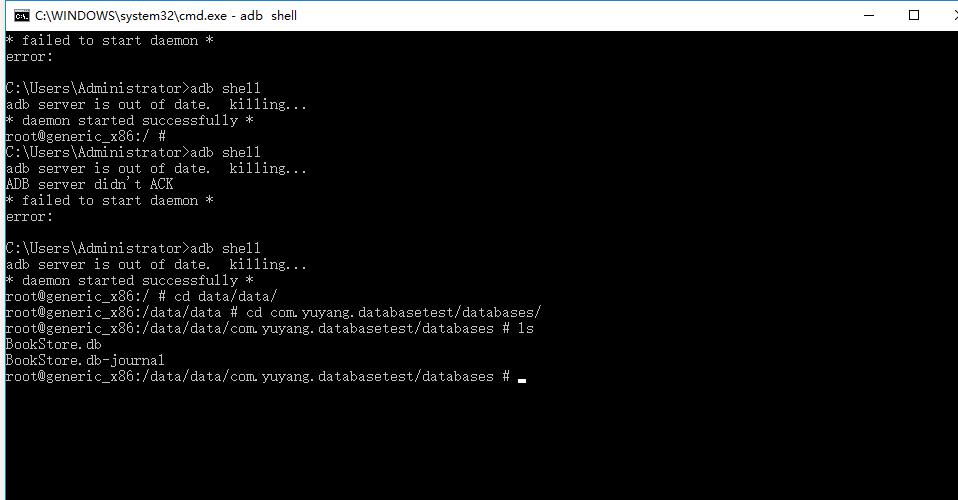
6)創建的數據庫放在 /data/data/”package name”/database/ 目錄下面
這里我們就創建一個數據庫實例:
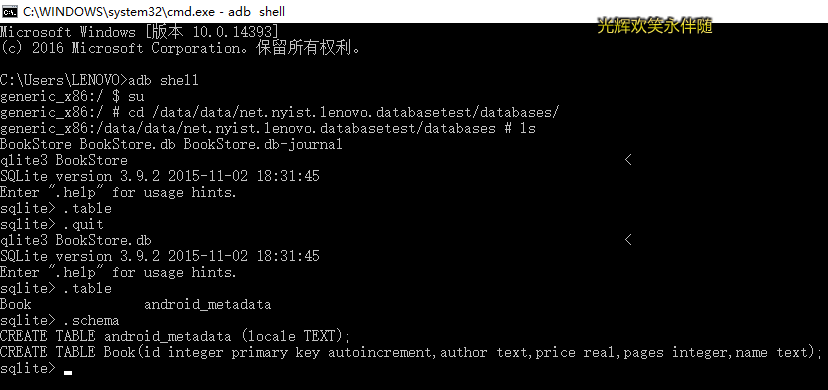
數據庫名稱: BookStore.db
添加一張表:Book
表中有id(主鍵) 、 作者、 價格、 頁數、 書名 等列
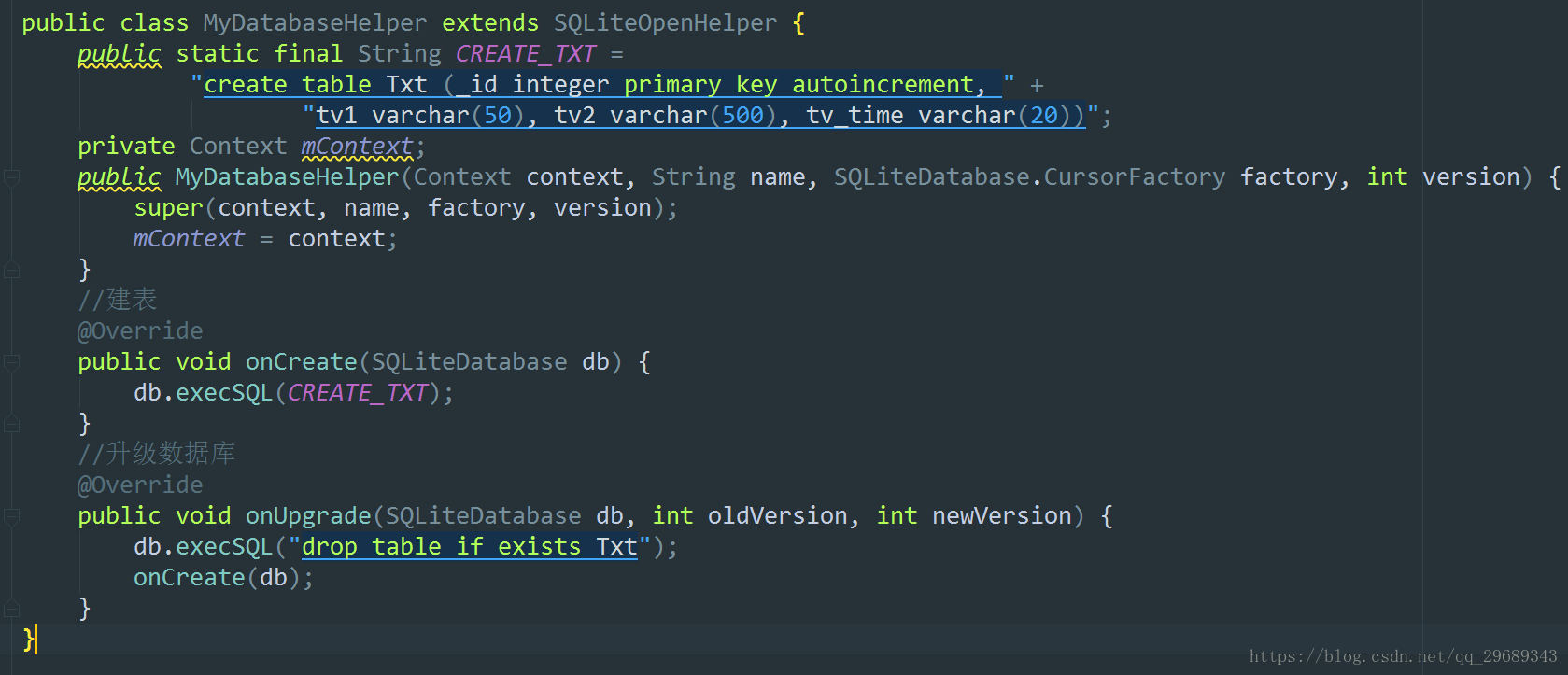
create table Book (
id integer primary key autoincrement,
author text,
price real,
pages integer,
name text
)SQLite 的數據類型:
integer 表示整型
real 表示浮點型
text 表示文本類型
blob 表示二進制類型
上述語句我們把primary key 列設為主鍵, 并用autoincrement 關鍵字表示id 列是自增長的。
3、一個示例
創建 一個數據庫 用于保存 學生的 : 姓名 性別 年齡 學號
4、代碼架構
5、主要代碼
activity_main.xml 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.menglux.mysqlitedata.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/creat_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="創建"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/add_one_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="添加 one"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/add_two_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="添加 two"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/update_one_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="修改 one "
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/search_all_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="查找全部"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/search_condition_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="條件查找"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/delate_two_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="刪除 two"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/delate_all_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="刪除 全部"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java
package com.example.menglux.mysqlitedata;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private String TAG = "MainActivity: ";
private Button buttonCreat, buttonAddOne, buttonAddTwo, buttonUpdate,
buttonSearchAll, buttonSearchCondition,buttonDelateTwo,buttonDelateAll;
private SQLiteDatabase db;
private DataBaseOperation dop;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initvView(); //初始化組建信息
}
//初始化組建信息
private void initvView() {
buttonCreat = (Button) findViewById(R.id.creat_id);
buttonAddOne = (Button) findViewById(R.id.add_one_id);
buttonAddTwo = (Button) findViewById(R.id.add_two_id);
buttonUpdate = (Button) findViewById(R.id.update_one_id);
buttonSearchAll = (Button) findViewById(R.id.search_all_id);
buttonSearchCondition = (Button) findViewById(R.id.search_condition_id);
buttonDelateTwo = (Button) findViewById(R.id.delate_two_id);
buttonDelateAll = (Button) findViewById(R.id.delate_all_id);
buttonCreat.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonAddOne.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonAddTwo.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonUpdate.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonSearchAll.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonSearchCondition.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonDelateTwo.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonDelateAll.setOnClickListener(this);
dop = new DataBaseOperation(this, db); //實例化數據庫對象
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch(v.getId()) {
case R.id.creat_id: //創建數據庫,若已經存在就打開
dop.create_db();
dop.close_db();
break;
case R.id.add_one_id: //向數據庫添加 一個學生 one : 姓名 性別 年齡 學號
dop.create_db();
dop.insert_db("lum","boy",26,"528");
dop.close_db();
break;
case R.id.add_two_id: //向數據庫添加 一個學生 two : 姓名 性別 年齡 學號
dop.create_db();
dop.insert_db("who","girl",24,"520");
dop.close_db();
break;
case R.id.update_one_id: // 更新學生 根據學號 更新 one 的 姓名 年齡
dop.create_db();
dop.update_one("lumeng",28,"528");
dop.close_db();
break;
case R.id.search_all_id: //查找數據庫全部信息
dop.create_db();
Cursor cursor = dop.query_db();
if (cursor.getCount() > 0) { //如果數據庫里查詢到數據
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {// 光標移動成功
String str_name = cursor.getString(cursor
.getColumnIndex("name")); // 獲得姓名
String str_sex = cursor.getString(cursor
.getColumnIndex("sex")); // 獲得性別
int int_age = cursor.getInt(cursor
.getColumnIndex("age")); // 獲得年齡
String str_id = cursor.getString(cursor
.getColumnIndex("id")); // 獲得學號
System.out.println(TAG + "姓名: " + str_name + " 性別:" + str_sex + " 年齡:" + int_age
+ " 學號:" + str_id);
}
}
dop.close_db();
break;
case R.id.search_condition_id: //依照性別 boy 查找 學生
dop.create_db();
Cursor cursor_sex = dop.query_sex("boy");
if (cursor_sex.getCount() > 0) { //如果數據庫里查詢到數據
while (cursor_sex.moveToNext()) {// 光標移動成功
String str_name = cursor_sex.getString(cursor_sex
.getColumnIndex("name")); // 獲得姓名
String str_sex = cursor_sex.getString(cursor_sex
.getColumnIndex("sex")); // 獲得性別
int int_age = cursor_sex.getInt(cursor_sex
.getColumnIndex("age")); // 獲得年齡
String str_id = cursor_sex.getString(cursor_sex
.getColumnIndex("id")); // 獲得學號
System.out.println(TAG + "姓名: " + str_name + " 性別:" + str_sex + " 年齡:" + int_age
+ " 學號:" + str_id);
}
}
dop.close_db();
break;
case R.id.delate_two_id: //根據學號 刪除學生 two
dop.create_db();
dop.delate_two("520");
dop.close_db();
break;
case R.id.delate_all_id: //刪除 全部學生
dop.create_db();
dop.delate_all();
dop.close_db();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
DataBaseOperation.java
package com.example.menglux.mysqlitedata;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* Created by lum on 2018/5/6.
*/
public class DataBaseOperation {
private final String TAG = "DataBaseOperation: ";
private SQLiteDatabase db;
private Context context;
public DataBaseOperation(Context context, SQLiteDatabase db) {
this.db = db;
this.context = context;
}
//數據庫的打開或創建 db name student.db
public void create_db() {
db = SQLiteDatabase.openOrCreateDatabase(context.getFilesDir().toString() + "/student.db", null);
if (db == null) { //判斷數據庫是否創建成功
System.out.println(TAG + "數據庫創建失敗" );
}
//創建表,tab name 名稱為 record ,主鍵id
db.execSQL("create table if not exists record(_id integer primary key autoincrement,"
+ "name varchar(30)," // 姓名
+ "sex text," //性別
+ "age integer," //年齡
+ "id text" + ")");//學號
System.out.println(TAG + "數據庫創建成功" );
}
//插入備忘錄信息到數據庫
public void insert_db(String name,String sex,int age,String id) {
db.execSQL("insert into record(name,sex,age,id) values('"
+ name //姓名
+ "','"
+ sex //性別
+ "','"
+ age //年齡
+ "','"
+ id //學號
+ "');");
System.out.println(TAG + "插入新的數據庫信息" );
}
//根據學號 更新學生 one 的 姓名 年齡
public void update_one( String name,int age , String id) {
db.execSQL("update record set name='" + name
+ "',age='" + age
+ "'where id='" + id + "'");
System.out.println(TAG + "修改學生 one 資料" );
}
//查詢所有內容
public Cursor query_db() {
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from record", null);
System.out.println(TAG + "查找全部數據庫信息" );
return cursor;
}
//根據性別查找
public Cursor query_sex(String sex) {
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from record where sex='" + sex
+ "';", null);
System.out.println(TAG + "根據性別查找" + sex );
return cursor;
}
// select * from 表名 where 學號 between '開始學號' and '結束學號' // 學號段查詢
public Cursor query_duing_id(String startid, String endid) {
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from record where id >='" + startid + "'and timeedit<='"
+ endid + "';", null);
System.out.println(TAG + "學號段查詢" );
return cursor;
}
// select * from 表名 where content like '%abc%' //模糊查詢 查找全表中 姓名包含 關鍵字的學生
public Cursor query_content(String keword) {
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select * from record where name like '%"
+ keword + "%';", null);
System.out.println(TAG + "關鍵字模糊查詢" );
return cursor;
}
//根據學號 刪除 學生 two
public void delate_two( String id ) {
db.execSQL("delete from record where id='" + id + "'");
System.out.println(TAG + "刪除學生 two");
}
//刪除表全部內容 不刪除表
public void delate_all( ) {
db.execSQL("delete from record" );
System.out.println(TAG + "清空表內容");
}
// 關閉數據庫
public void close_db() {
db.close();
System.out.println(TAG + "關閉數據庫");
}
}可用于在一個activity 創建數據庫,在另一個activity 打開數據庫
文件參考:
android之存儲篇SQLite數據庫讓你徹底學會SQLite的使用
https://blog.csdn.net/jason0539/article/details/10248457
智能推薦
Android中的SQLite數據庫存儲
SQLlite是一款輕量級的關系型數據庫, 作為Android系統內置的數據庫, 它的運算數度非常快,占用資源少,通常只需幾百KB的內存就足夠,SQLite不像其他關系型數據庫擁有眾多繁雜的數據類型,它的數據類型很簡單,integer 表示整型, real表示浮點型, text表示文本類型, bolb表示二進制型。 此處出示一個SQLite數據庫存儲的案例: SQLite...
SQLite數據庫存儲(一)【安卓學習筆記】
對于MODE_PRIVATE,MODE_APPEND兩種模式,對寫文件的影響有什么不同? MODE_PRIVATE:該文件只能被當前程序讀寫,會把原來的內容覆蓋掉 MODE_APPEND:該文件的內容可追加,不會把原來的內容覆蓋掉,新寫的內容追加在文件后面 但是對于修改文件中的部分內容,應該怎么做呢?這就需要我們用到SQLite數據庫 主要內容: 創建和打開一個SQLite 數據庫 SQLite數...
17讀書筆記之SQLite數據庫存儲
SQLite數據庫存儲 創建數據庫 Android管理數據庫提供了一個SQLiteOpenHelper幫助類。 借助這個類就可以簡單地對數據庫進行創建和升級。下面學習SQLiteOpenHelper的基本用法。 首先SQLiteOpenHelper是一個抽象類,我們要是用的話,需要創建一個自己的幫助類去繼承它。SQLiteOpenHelper中有兩個抽象方法。 onCreate()和onUpgra...
使用Android studio實現SQLite數據庫存儲
使用Android studio實現SQLite數據庫存儲 題目 代碼 XML代碼(1) XML代碼(2) JAVA代碼(1) JAVA代碼(2) JAVA代碼(3) 運行結果 題目 1.要求按圖1完成設計,此界面為啟動界面。其中Spinner中的數據為:語文,數學,英語,歷史,生物。Spinner使用適配器綁定數據。 2.當點擊“添加成績”按鈕時,先判斷SQLite中是否...
【鼠】安卓學習雜記(十三)——Android數據存儲之SQLite數據庫存儲
一、適用場景 適用于存儲一些復雜的關系型數據。 二、概述 輕量級嵌入式數據庫引擎,它支持SQL 語言,并且只利用很少的內存就有很好的性能。可存儲大量的數據。 Android SQLite對我目前的安卓學習水平而言,還是比較復雜的,在此處暫不做詳細闡述,僅以此時使用狀態闡述。 三、使用步驟 第一步:創建MyDatabaseHelper繼承SQLiteOpenHelper 第二步:在MainActiv...
猜你喜歡
第一行代碼之SQLite數據庫存儲
SQLite數據庫存儲 6.3.1 創建數據庫 Android專門提供了一個 SQLiteOpenHelper幫助類對數據庫進行創建和升級 SQLiteOpenHelper需要創建一個自己的幫助類去繼承它并且重寫它的兩個抽象方法,即 onCreate() 和 onUpgrade() SQLiteOpenHelper 中有兩個重要的實例方法:getReadableDatabase() 和 getWr...
《第一行代碼》 6.4 SQLite數據庫存儲
特點:適用于存儲大量復雜的數據。 6.4.1 創建數據庫 1. SQLiteOpenHelper幫助類(抽象類),助于數據庫的創建和升級 (1)兩個構造方法供選,一般選參數少的那個: SQLiteOpenHelper(參數1,參數2,參數3,參數4) ...
SQLite數據庫存儲(創建數據庫,升級數據庫和增刪改查四種基本操作)
我們Android系統是內置了數據庫的,在SDK中的platform-tools文件夾中。 SQLite是一款輕量級的關系型數據庫,它的運算速度非常快,占用資源很少,通常只需要幾百k的內存就足夠了,因此比較適合在移動設備上使用。 創建數據庫 首先我們需要創建一個自己的幫助類,去繼承于SQLiteOpenHelper這個幫助類。SQLiteOpenHelper中有兩個抽象方法,一個是onCreate...